Types of Rapid Tooling
The term Rapid Tooling (RT) is literally described as a process that either uses Rapid Prototyping (RP) process to fabricate the mold directly or utilizes a Rapid Prototyping (RP) model as a pattern to produce a mold quickly.
Generally, Rapid Tooling (RT) can be classified in 2 main types – Direct and Indirect. Some will gain benefit from Direct RT but others will find Indirect RT suits them the most.
In order to make the most of Rapid Tooling process, this guideline will summarize and differentiate between these two types of Rapid Tooling in order to help product designers or entrepreneurs to decide which is the best option for their prototyping process.
Direct Rapid Tooling
Indirect Rapid Tooling
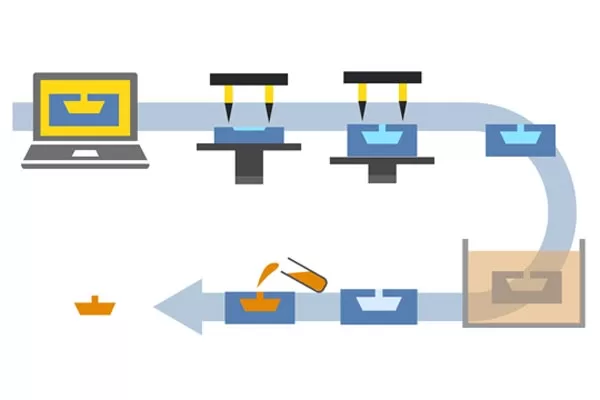
1. Create 3D CAD Model of a mold or tool.
2. Send 3D CAD model file to machine to make the mold or tool.
3. The mold or tool can be used directly to make prototypes.
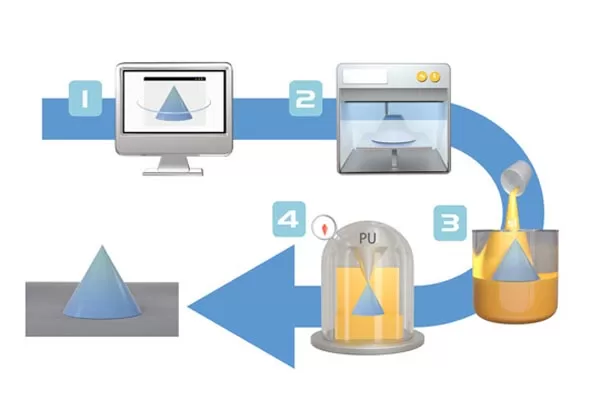
1. Create 3D CAD Model of a master pattern.
2. Send 3D CAD model file to machine to make the master pattern.
3. Make mold or tool based on master pattern.
4. Prototypes can then be created using the mold tool.
| Direct RT | Indrect RT | |
| Pros: |
1. Less steps involved. |
1. The master pattern is very durable and likely to invest in one master pattern only (unless design changes). |
| Cons: |
1. May need to create multiple molds if different materials needed to be tested for prototypes. |
1. Slightly more time consuming if compare to direct rapid tooling. |
| Typical Application |
Plastic Injection Molding Tooling (PIM) |
Silicone Rubber Tooling (Vacuum Casting) |
Avoiding Costly Investment or Delay
Which type of Rapid Tooling should you select? It basically depends on the combination of your design complexity, product development stage, budget, timeline, materials, tolerances and so on. Always speak to engineering experts to discuss your requirements from the beginning before your project commences. Proper upfront communication with manufacturer will lead to efficient manufacturing process and result in high return in your investment.
