By now you must know that CNC machining is used in industrial and manufacturing application. But what exactly does it imply and what a CNC machining is?
We will discuss it in the following passages. So take a look.
Computer numerical control is a subtractive manufacture procedure that usually employs multiple automated controls & machinery in order to remove the material layers from the work piece or blank – also known as the stock piece and delivers a customized design part.
The entire procedure is appropriate for a variety of materials that include but are not limited to composites, foam, wood, plastics, glass, metals, and so on. It has application in a wide range of industries like CNC machining aerospace, huge CNC machining, and so on.
CNC machining stands as opposed to the additive manufacturing procedure like that of 3D painting and formative manufacturing procedure like that of the liquidated injection mold. Let’s briefly take a look at these two processes. The subtractive procedure removes the layers of the substance from the stock piece in order to produce a custom design and shape. On the other hand, the additive process usually gather all the layers of materials in order to deliver the required shape, The formative process then displace and deform the stock substance into the desired design.
The automatic behaviour of CNC machining allows the manufacture of high accuracy and precision, cost effectiveness, simplicity of parts and also fulfils medium volume and one-off production runs. But the problem is though CNC machining delivers various advantages over any other manufacturing procedure, its intricacy and complexity is quite higher for part designing and the cost efficacy of delivering the complicated parts is limited.
Every kind of the manufacturing procedure has several disadvantages and advantages. Here, let’s take a look at the brief outline of the process and its components.
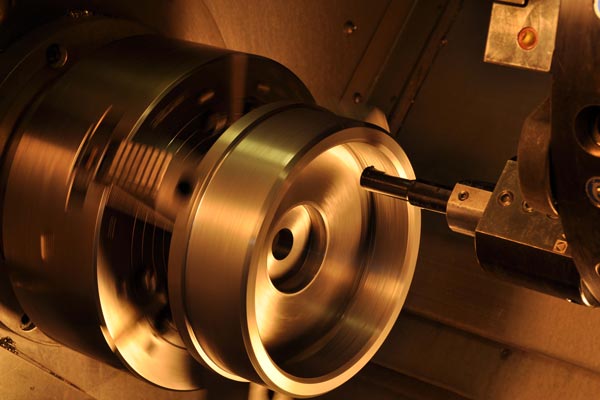
CNC machines
CNC machining is that type of the manufacturing procedure that uses computer controls while operating and manipulating the machines and cutting the tools while shaping the stock materials like foam, metal, plastic, composite and others for custom design.
Though CNC machining has various operations and capabilities, the basic principles of the procedure largely remain similar throughout all of them. Here, take a look at the basic CNC machining procedure that includes the following steps:
- Design the CAD model
- Convert the CAD file into a CNC program
- Prepare the CNC machine
- Execute the machine operation
CNC machining procedure starts with creating a 2D or 3D vector or solid CAD design. It can be in house or by a CAM or CAD designing company. Computer operated design software is generally used here that lets the manufacturers and designers to create a model through various technical specifications like geometries and dimensions. This ends in producing various parts of the products.
Design of the CNC machined parts are limited in their capabilities of the CNC tools and machinery. For instance, many of the CNC machine tools are cylindrical and thereby the part geometries required through the CNC machining procedure are quite restricted since the tools create a curved corner section.
Further, the properties of the machined substances, work holding capacity of the machines, as well as the tool designs limit the scope of designing, like the maximum part size, minimum thickness of the part, and complexity and inclusion of the internal features and cavities.
Once the entire CAD design is finished, the designers export it to the CNC file like IGES or STEP format.
This formatted CAD design then gets operated through a certain program with the computer aided manufacturing software or the CAM software and finally delivers the part geometry before producing the digital programming code that helps in controlling the CNC machine to manipulate the tools. It finally results in a custom designed part.
CNC machines use various programming language such as M code and G code. One of the most common CNC programming language is the geometric or general code, commonly referred to as the G code. It controls where, how, and when the machining tools can move, when to turn it on or off, which path to take, how to travel to a particular destination, and its speed, maintaining what space throughout the workpiece, and so on. M code, the short form of the miscellaneous function code controls various auxiliary machine and functions, like the automated removal, replacement of the machine, and its end production.
Just when the CNC program gets generated the operator uses it to the CNC machine.
Before the operator starts the CNC programming, it has to prepare the machine for the potential operation. The preparation process include fixing the work holding piece into the machine directly, on the machinery splindles, and affixing the necessary tooling for instance end mills and drill bits.
So, you know the basic operation of CNC machining. Share your thoughts with us.
